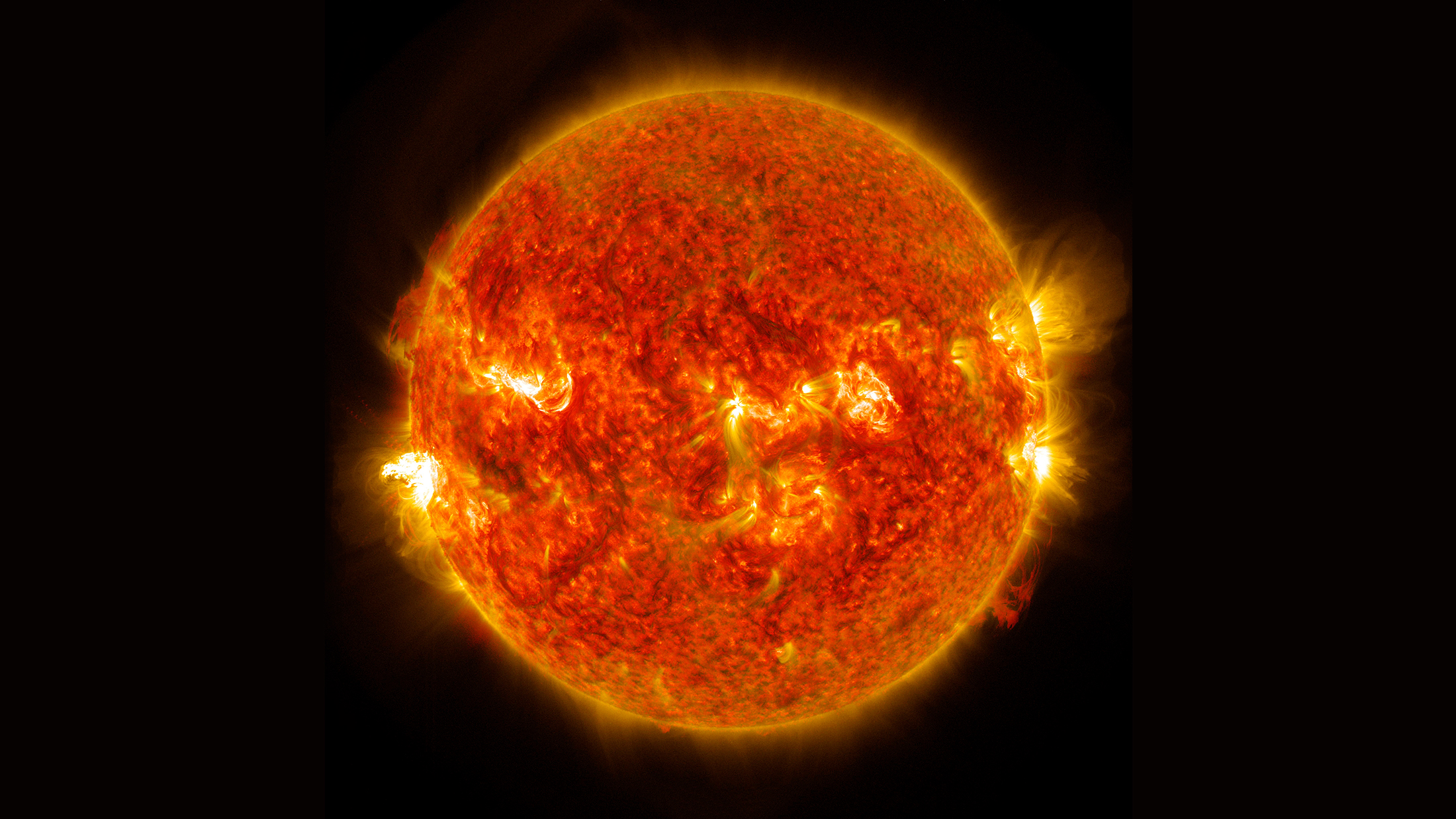
The science of heliophysics examines the sun and its connection to the solar system, including its influence on space, the planets, and more.
A team of researchers from Predictive Science Incorporated – a San Diego-based company whose research programs focus on models and methods to help answer scientific questions about the physics of the sun – recently used Expanse at the San Diego Supercomputer Center at UC San Diego to investigate future space weather.
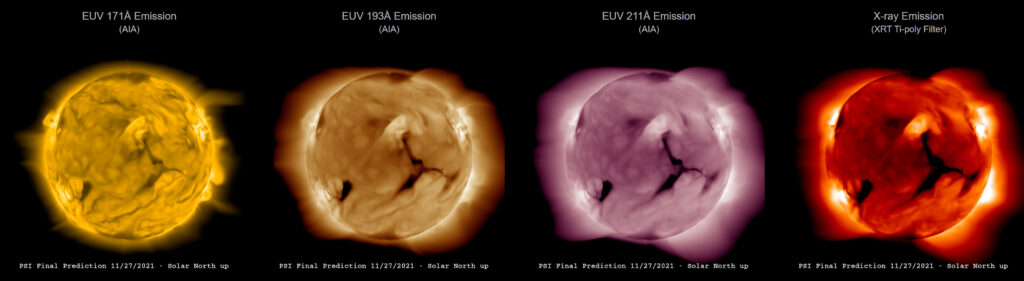
With the computing capacity of Expanse and an abundance of solar wind observations, the team was able to model the structure and evolution of the sun’s outer atmosphere. Their results, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, showed that solar activity is likely to remain relatively mild over the next decade.
The study, which relied on both observations of the solar wind and the researcher team’s interpretation using the results of global numerical models run on Expanse, suggested that the sun has been entering an ever lower state of activity, meaning that the effects of space weather for the next several years will be less dramatic than during more active cycles.
Every 11 years, the sun goes through a cycle of changing solar radiation, sunspots, solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Understanding how the sun’s magnetic field drives these changes is a fundamental goal for heliophysics.
Pete Riley, research scientist, Predictive Science Inc.
You can read more about this story here (Published Nov. 7, 2022): Expanse Supercomputer Used to Illustrate the Future of Solar Storms
Project Details
Institution: Predictive Science Incorporated
University: San Diego Supercomputer Center, UC San Diego
Funding Agency: NASA (80NSSC18K0100, NNX16AG86G, 80NSSC18K1129, 80NSSC18K0101, 80NSSC20K1285, 80NSSC18K1201, and NNN06AA01C), NOAA (NA18NWS4680081), and the U.S. Air Force (FA9550-15-C-0001).
Allocation Number: 1854790
The science story featured here is enabled by the ACCESS program, which is supported by National Science Foundation grants #2138259, #2138286, #2138307, #2137603, and #2138296.


